7QC Tools for Problem Solving | What are 7 QC Tools
7QC Tools for Problem Solving | What are 7 QC Tools
7QC Tools for Problem Solving techniques are generally used in manufacturing, Non-manufacturing industries, and service sectors to resolve problems.
Download 7-QC Tools Template/ Format
Definition and History:-
The 7QC Tools (Also Known as “Seven Basic Tools of Quality”) originated in Japan. First emphasized by Kaoru Ishikawa, a professor of engineering at Tokyo University and the father of “quality circles”. These tools are used to solve critical quality-related issues. You can use the 7 basic tools of quality to help understand and solve problems or defects in any industry. With the help of Excel, you can plot the graphs / Diagrams to resolve the daily quality problems. I will help you to understand the basic ideas and knowledge of 7QC Tools and their usage.
For solving problems seven QC tools are used Pareto Chart, Cause & Effect Diagram, Histogram, Control Charts, Scatter Diagrams, Graphs/Process Flow Diagram, and Check Sheets. All these tools are important tools used widely in the manufacturing field to monitor the overall operation and continuous process improvement. seven QC tools are used to find out the Root cause of the problem and implement the action plan to improve the process efficiency.
7QC tools are:-
- Pareto Chart
- Cause and effects diagram
- Histogram
- Scatter Diagram
- Control Chart
- Check Sheet
- PFD(Process Flow diagram)/Graphs

Benefits of 7QC Tools:-
- Improve management decisions.
- Simple and easy for implementation
- Continuous quality improvement
- Quick results
- Enhances customer satisfaction through improved quality product
- Reduce cycle time and improve efficiency
- Control cost of poor quality / Cost of quality
- Reduce defects and optimize the production
- Reduce variations and improve the quality of Products
- Encouragement of teamwork and confidence
- Enhancement of customer focus.
Pareto Chart:-
A Pareto Chart is named after the Italian Economist Vilfredo Pareto. It is a type of chart that contains both bars and a line graph, where the individual values are represented in the bar graph in descending order (largest to smallest value) and the cumulative percentage is represented in the line graph.
Click here to learn “How to Plot Pareto Chart In Excel”.
Understanding the Pareto Chart principle (The 80/20 rule):
The Pareto principle is also known as the 80/20 rule derived from the Italian Economist Vilfredo,
The principle is understood as –
20% of the input creates 80% of the results
Or
80 % of the effects come from 20% of the causes.
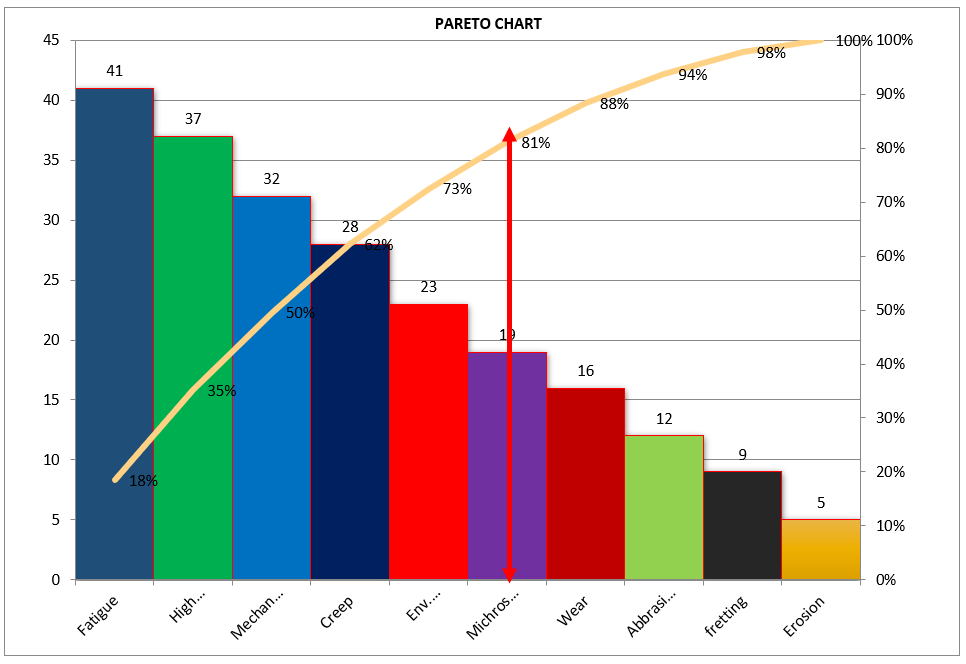
[Figure-1]
In the above Pareto Chart[Figure-1], we can see the cumulative% in the line graph, According to the Pareto Chart principle 80/20 rule, the 80% cumulative in the line graph is filling under the low hardness, which means BH, Damage, SH and Low hardness defers are coving the 80% of contribution over total types of defects. And those 80 % of contributions were due to the 20% caused.
Histogram:-
The histogram is one of the 7QC tools, which is the most commonly used graph to show frequency distribution.
Helps summarize data from a process that has been collected over a period of time.
Click here to know the “How to Plot Histogram in Excel:
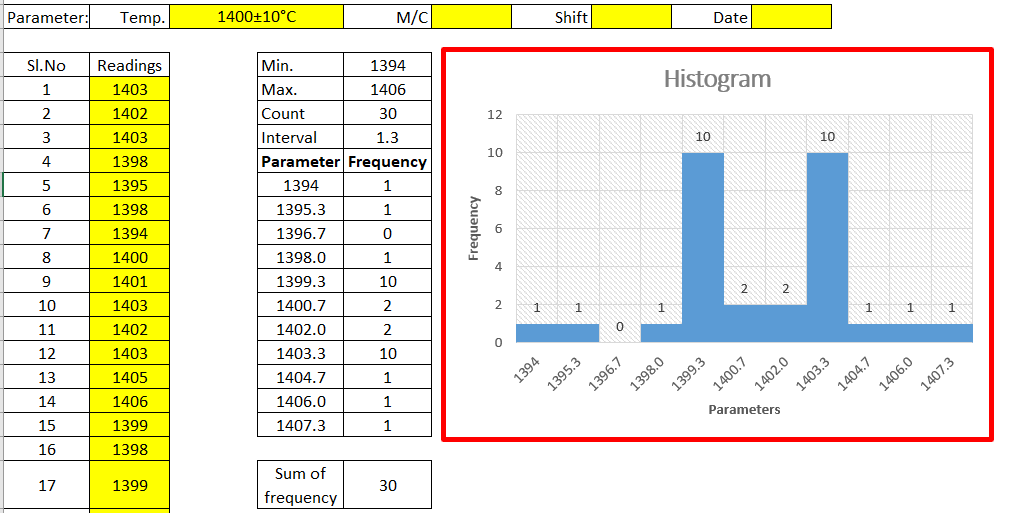
[Figure-2]
Fish-bone Diagram/Cause and Effects /Ishikawa Diagram:-
The cause and Effects Diagram looks like a fish that’s why it’s called Fish-bone Diagram, also called the Ishikawa diagram.
It’s a visualization tool for categorizing the potential causes of a problem in order to identify its root causes.
CFT members are identifying the potential cause through the Brainstorming process of individuals and together.
The Potential cause is related w.r.t below as
- Machine
- Manpower
- Environment
- Method
- Materials
- Measurement
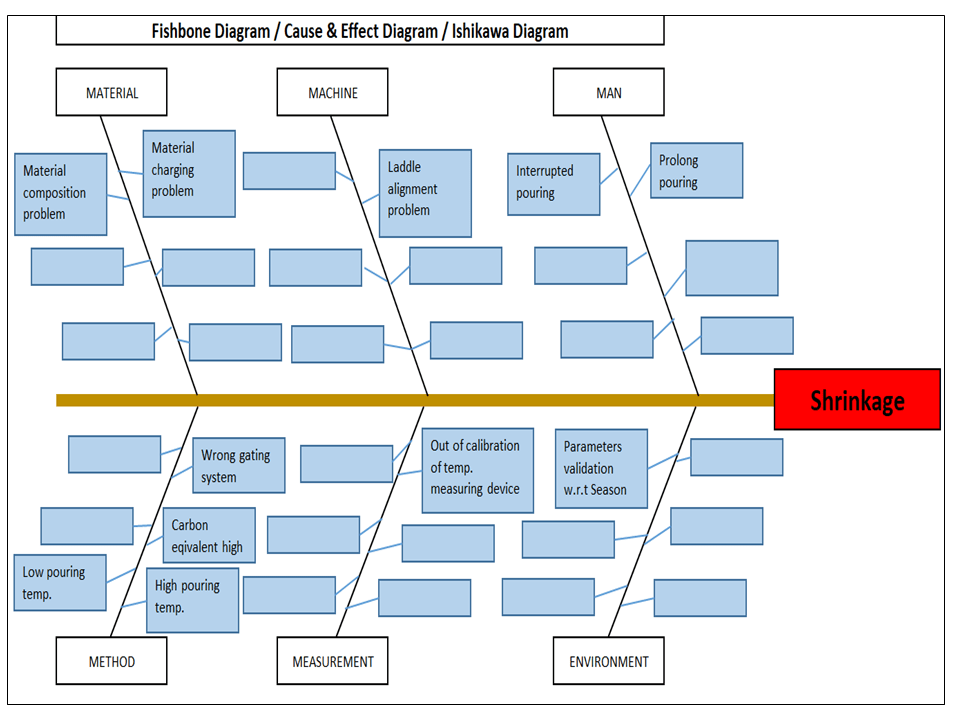
[Figure-3]
Scatter diagram:-
The scatter diagram graphs pairs of variable data, with one variable on each axis, to look for a relationship between them. If the variables correlate, the points will fall along a line or curve. The better the correlation, the more points will strongly cluster to the line. It generally gives the idea of the correlation between the variables.
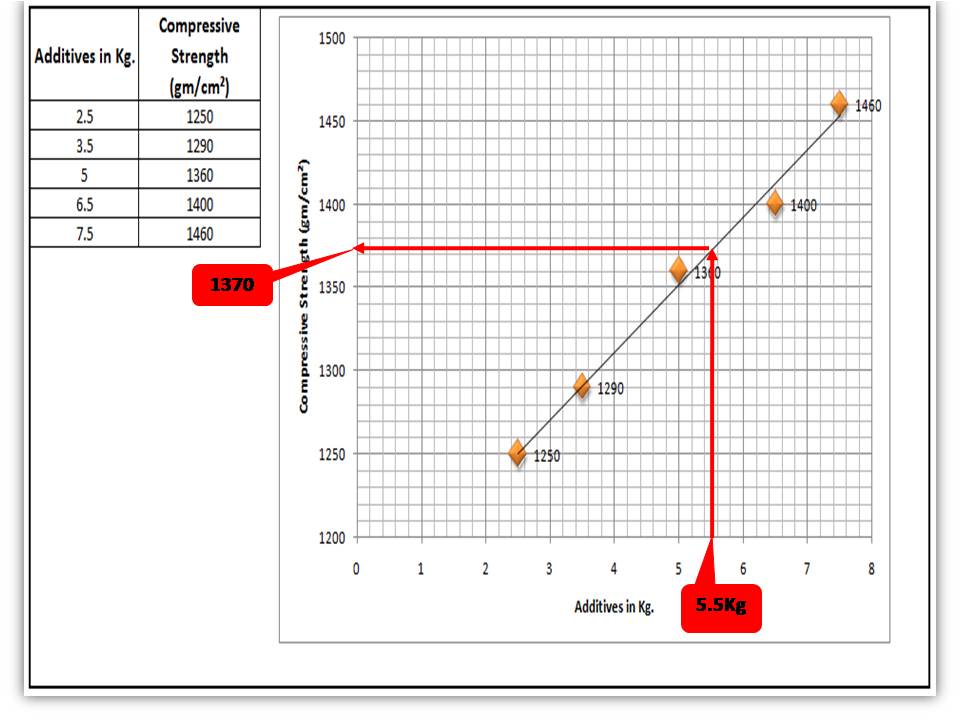
[Figure-4]
In the above figure-4, the positive and Negative correlation is only due to the direction, and in both the correlation, points are clustered to the line but in the last figure in figure-4, Points are not clustered to the line but spread over the X and Y-axis.
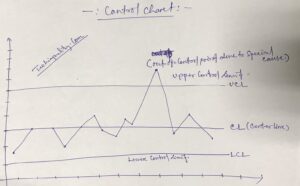
Control Chart:-
A line on a control chart is used as a basis for judging the stability of a process. If the observed points are beyond a control limit then it is evidence that special causes are affecting the process.
Control Charts can be used to monitor or evaluate a process.
There are basically two types of control charts, those for variable data and those for attributes data.
Click here to learn more about the Control Chart and Statistical Process Control.
Benefits:-Higher Quality, Lower Unit Cost, Higher effective Capability, etc.
Selection of Control Charts based on Attribute / Variable Type Data:-
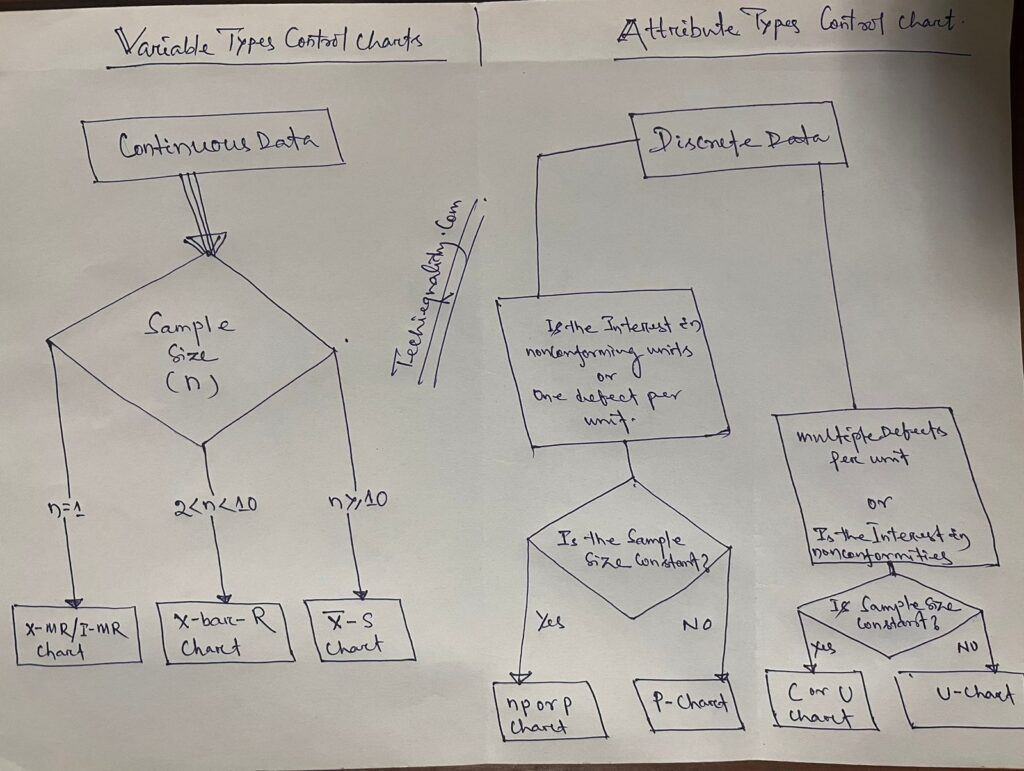
Calculation of Average and Range Charts-
Click here to know the details.
The formula of the Attributes Control Chart:-
Click here to learn the formula and calculation.
Nomenclature of Control Chart:-
Check Sheet:-
Check Sheet is a simple document used for collecting data in real time. Variable or Attribute type data is collected through a Check sheet. A check sheet generally helps to make the decision on the basis of a fact and to collect the data for analysis and evaluation.
Sample check Sheet:-
| Logo | Title:-……… | Format No- Issue no-… rev. no- Date- | |
| Parameters | Specification | Observations | Remarks |
| Checked by:- Verified by:- |
Process Flow diagram/Graphs:-
A process flow diagram is a diagram used to indicate the general flow of plant processes and equipment.
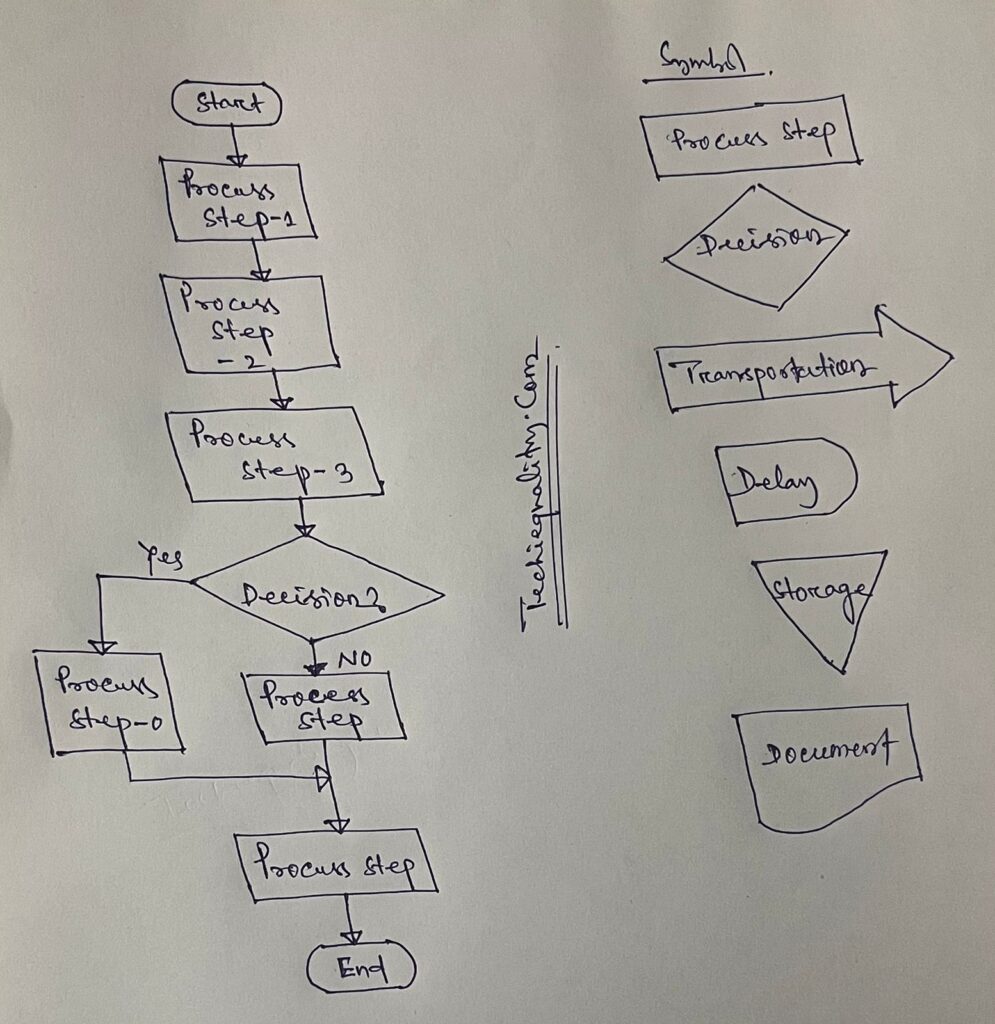
The 7QC tools are the most commonly used tool in the industry for improvement, With the help of the 7QC tools you can understand the process/activities, analyze the data, and interpret the result/graph/output.
FAQ:
Which are the 7 QC tools?
The seven QC tools are
- Pareto Chart
- Fishbone diagram
- Histogram
- Scatter Diagram
- Control Chart
- Check Sheet
- PFD(Process Flow diagram)/Graphs /Stratification
Useful Article:
why why analysis methodology | 5-why analysis step by step guide
Rework vs Repair |IATF Requirement for Control of Reworked/ Repaired Product
How to plot the Run Chart in Minitab
Run Chart Example | Concept & Interpretation of Result with Case Study | Industrial Example:
Thank you for reading..keep visiting Techiequality.Com
I hope the above article “7QC Tools for Problem Solving” is useful to you…
Popular Post:


